When it comes to the world of wine, there are two prominent players that stand out – red and white. These two types of wine differ in various aspects, ranging from their color and grape varieties used to their fermentation process and flavor profiles. Understanding the distinctions between red and white wine can enhance your appreciation and enjoyment of this timeless beverage.
This brief introduction will explore the key differences between red and white wine, including their color variations, tannin levels, serving temperature recommendations, and food pairing suggestions. Additionally, we will delve into the health benefits of both types of wine and showcase popular examples of red and white wines. So, join us on this journey as we uncover the nuances that set red and white wine apart.
Key Learnings
- Red wines obtain their deep hues from prolonged skin contact during fermentation, while white wines are made by fermenting the juice without the skin, resulting in a lighter color.
- Red wines are typically made from dark-skinned grapes like Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Pinot Noir, while white wines are usually made from light-skinned grapes such as Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, and Riesling.
- Red wines are rich, bold, and full-bodied with flavors of dark fruits, spices, and earthy undertones, while white wines are lighter, crisper, and more refreshing with flavors of citrus fruits, tropical fruits, and floral notes.
- Red wines generally have higher tannin levels compared to white wines, which contribute to the structure and aging potential of the wine. Red wines can age longer and develop complex flavors and aromas, while white wines are often enjoyed young without extensive aging.
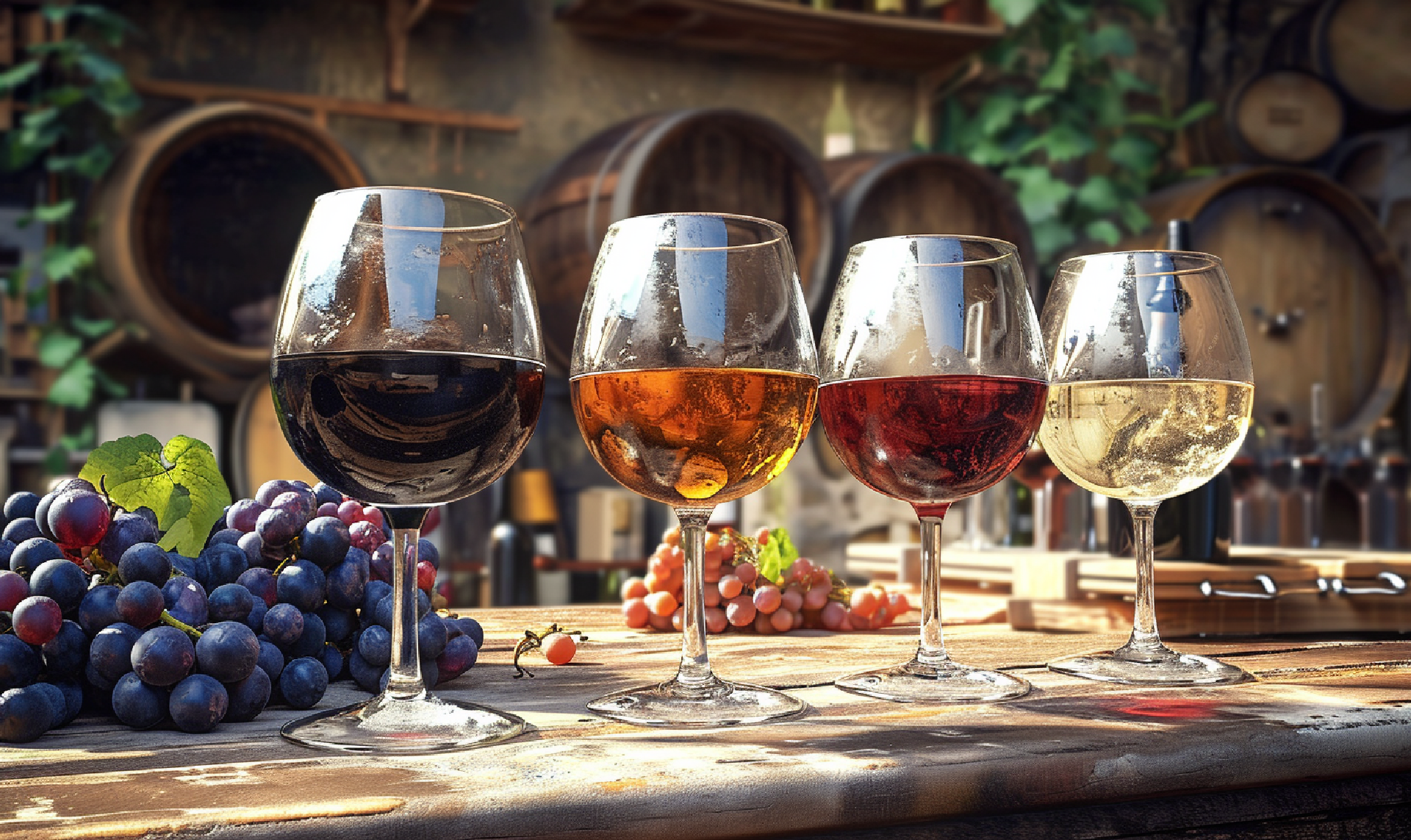

Color Variations
Red and white wines differ in color due to the time they spend in contact with grape skins during the winemaking process. The color variations in wine result from the pigments in the grape skins. Red wines obtain their deep hues from prolonged skin contact, as the grape skins contain anthocyanins responsible for red, purple, or even blue colors.
On the other hand, white wines are made by fermenting the juice without the skins, resulting in a lighter color. The absence of skin contact means that the white wines lack the anthocyanin pigments found in red wines. Understanding the color variations is crucial for wine enthusiasts, as it can provide insights into the grape variety, region, and even the aging potential of the wine.
Grape Varieties Used
When it comes to the grape varieties used in red and white wines, there is a marked difference. Red wines are typically made from dark-skinned grapes, such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Pinot Noir, while white wines are usually made from light-skinned grapes like Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, and Riesling. This distinction in grape varieties contributes to the contrasting flavor profiles and characteristics found in red and white wines.
Red vs. White Grapes
The selection of grape varieties used in red and white wines differs significantly, contributing to the contrasting characteristics of each type of wine. Red wines are typically made from darker-skinned grapes, such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Pinot Noir, while white wines are usually made from lighter-skinned grapes, such as Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, and Riesling. These grape varieties have different levels of tannins, acidity, and flavors, which influence the taste and structure of the final wine.
The production and aging processes for red and white wines also vary. Red wines are fermented with grape skins, which gives them their rich color and robust flavors, while white wines are typically fermented without the skins, resulting in a lighter, crisper taste. The choice of grape variety plays a crucial role in shaping the character and style of both red and white wines.
Flavor Profiles Differ
A significant distinction between red and white wines lies in the varying flavor profiles resulting from the utilization of different grape varieties. The choice of grape variety plays a crucial role in determining the wine’s taste, aroma, and overall character.
Grape varieties like Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Pinot Noir are commonly used in red wines. These red grape varieties contribute to rich, bold, and full-bodied wines. Red wines often exhibit flavors of dark fruits, such as blackberry and cherry, along with hints of spices and earthy undertones.
On the other hand, white wines are typically made from grape varieties like Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, and Riesling. These white grape varieties result in lighter, crispier, and more refreshing wines. White wines often showcase flavors of citrus fruits, tropical fruits, and floral notes.

The choice of grape variety also affects the color intensity of the wine. Red grape varieties lend their deep, ruby hues to red wines, while white grape varieties contribute to white wines’ pale straw or golden colors.
Furthermore, the grape variety used can also influence the aging potential of the wine. Certain grape varieties, like Cabernet Sauvignon, have the capacity to age well and develop more complex flavors over time. On the other hand, some white grape varieties are best enjoyed young and do not benefit from extensive aging.
Fermentation Process
The fermentation process is a crucial step in the production of both red and white wines. During this process, yeast interacts with sugar in the grape juice, converting it into alcohol. The temperature and length of fermentation also play a significant role in determining the characteristics and flavors of the final wine product.
Yeast and Sugar Interaction
During fermentation, yeast interacts with sugar to convert it into alcohol, contributing to the distinct characteristics of red and white wines. This interaction is influenced by the choice of yeast strains and the amount of sugar consumed. Here are two key points to consider:
- Yeast Strains: Different yeast strains have varying abilities to consume sugar and produce alcohol. Certain strains are preferred for red wine production because they can tolerate higher alcohol levels, resulting in robust and full-bodied wines. In contrast, white wines often utilize yeast strains that produce lower alcohol levels to preserve the delicate flavors and aromas.
- Sugar Consumption: The amount of sugar consumed by yeast during fermentation determines the wine’s residual sweetness. In the case of dry wines, yeast converts most of the sugar into alcohol, resulting in minimal residual sugar. However, fermentation is halted in the production of sweet wines before all the sugar is converted, leaving a higher residual sugar level and a sweeter taste.
Understanding the intricate interaction between yeast and sugar is crucial in crafting wines with specific characteristics, catering to the diverse preferences of wine enthusiasts.
Temperature and Fermentation Length
Throughout the fermentation process, the temperature at which the grapes are fermented and the time the fermentation is allowed to take place greatly influence the characteristics of red and white wines. Temperature control is a crucial aspect of winemaking, as it affects the rate of fermentation and the development of flavors and aromas.
Red wines are typically fermented at higher temperatures, around 77-86°F (25-30°C), which allows for greater extraction of color and tannins from the grape skins. On the other hand, white wines are fermented at lower temperatures, around 50-59°F (10-15°C), to preserve delicate aromas and flavors. Fermentation techniques, such as cold soaking and controlled cooling, are employed to maintain the desired temperature throughout the process.
The length of fermentation also plays a role in the final product, with longer fermentation periods often resulting in more complex and structured wines. The careful management of temperature and fermentation length is essential in producing wines that showcase the desired characteristics and reflect the winemaker’s vision.
Tannin Levels
Red wines generally have higher tannin levels compared to white wines. Tannins are a group of compounds found in the skins, seeds, and stems of grapes. They contribute to the structure and mouthfeel of the wine, giving it a drying and astringent sensation. Here are some key points to understand about tannin levels in red and white wines:
- Red wine aging: Tannins in red wines act as a natural preservative, allowing them to age longer than white wines. This aging process helps develop complex flavors and aromas, making red wines more suitable for cellaring.
- White wine sweetness: White wines typically have lower tannin levels because they are made from grape varieties with thinner skins and are often fermented without the skins. Instead, the focus is on capturing the natural sweetness and fruitiness of the grapes.
Understanding tannin levels can enhance your appreciation and enjoyment of both red and white wines.
Flavor Profiles
When it comes to wine, the flavor profile is a key factor in understanding the differences between red and white varieties. Red wines are known for their bold and robust flavors, often attributed to their tannin levels, which lend a dry and astringent taste. On the other hand, white wines are characterized by their bright acidity, giving them a refreshing and crisp quality.
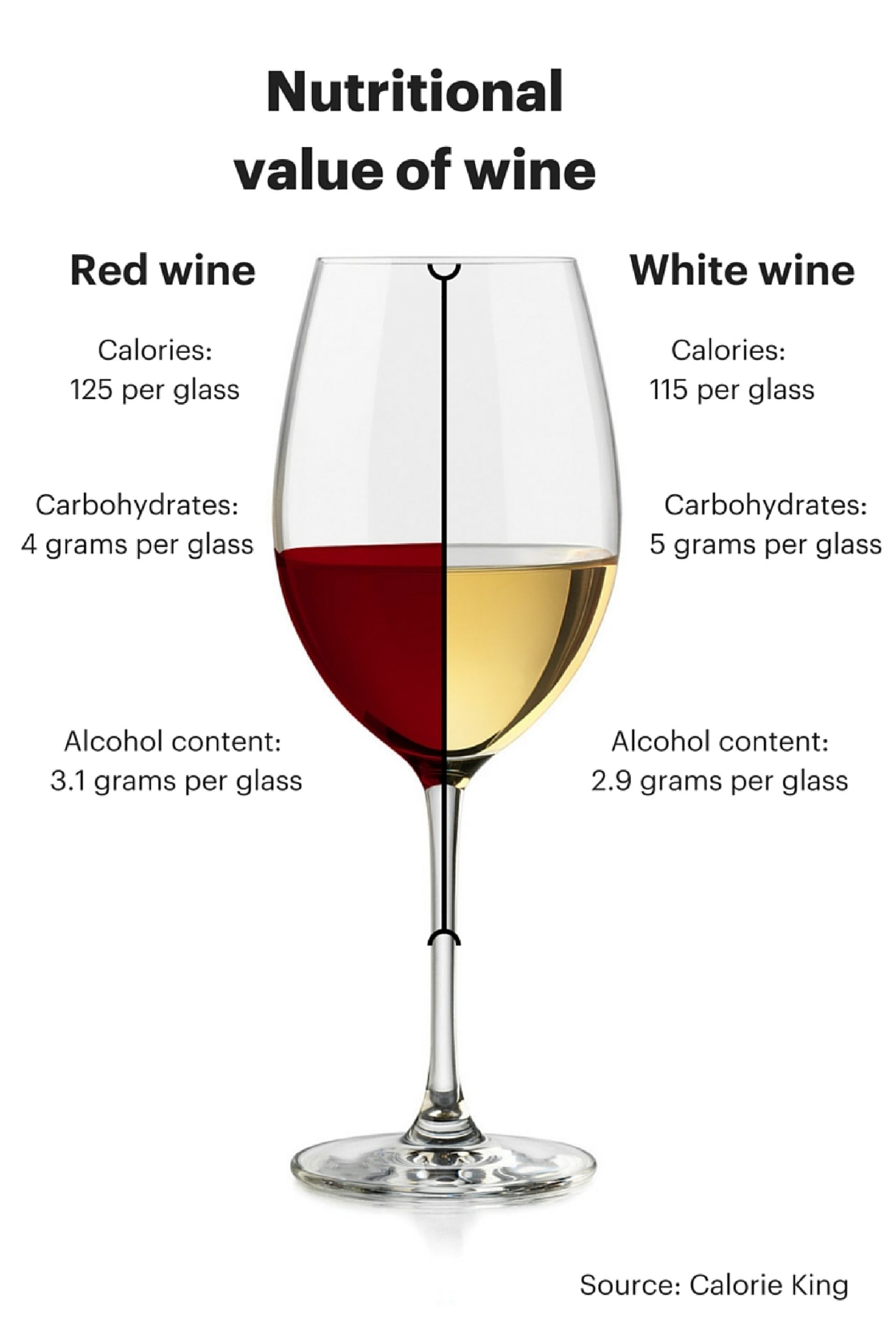
Additionally, red wines often exhibit fruit-forward notes, while white wines tend to showcase floral and citrus flavors. Understanding these flavor profiles is essential in selecting the right wine to complement different dishes and personal preferences.
Red Wine Tannins
In the realm of wine tasting, the flavor profiles of red wines are often characterized by the presence of tannins. These compounds, found in the skins, seeds, and stems of grapes, contribute to the structure and complexity of red wines. Here are two aspects of red wine tannins that are worth exploring:
- Red Wine Aging:
- Tannins in red wines play a crucial role in their aging potential. Over time, these tannins undergo polymerization, resulting in a smoother and more harmonious taste.
- The aging process allows the tannins to soften and integrate with other flavors, giving the wine a well-rounded and complex character.
- White Wine Oak:
- In contrast to red wines, white wines are often aged in oak barrels. This imparts subtle flavors and aromas, enhancing the wine’s complexity.
- Oak aging adds texture and depth to white wines, creating a creamy mouthfeel and notes of vanilla, spice, and toasted nuts.
Understanding the role of tannins in red wines and the influence of oak aging in white wines allows wine enthusiasts to appreciate the nuanced flavors and textures that each wine offers.
White Wine Acidity
White wine acidity plays a vital role in determining the flavor profiles of different varieties. The level of acidity in white wine can range from high to low, and it greatly affects the taste and overall experience of the wine. Higher acidity in white wine creates a crisp and refreshing sensation, while lower acidity can result in a smoother and rounder flavor. The table below highlights some popular white wine varieties and their corresponding acidity levels:
| White Wine Variety | Acidity Level |
|---|---|
| Sauvignon Blanc | High |
| Chardonnay | Medium |
| Riesling | High |
| Pinot Grigio | Low |
Understanding the acidity of white wine is important not only for taste preferences but also for white wine’s aging potential. The acidity helps preserve the wine and contributes to its longevity. Additionally, white wine has been associated with various health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health and antioxidant properties. So, indulge in a glass of white wine and savor its acidity and potential for your palate and well-being.
Fruit vs. Floral
Understanding the flavor profiles of white wine varieties extends beyond acidity, as the distinction between fruit and floral notes adds another layer of complexity to the overall taste experience. When it comes to white wine, the choice between fruit and floral flavors can greatly impact the enjoyment of the wine. Here are two key points to consider:
Fruit vs. Floral
- Fruit notes: White wines with fruit flavors often exhibit characteristics such as citrus, apple, pear, or tropical fruits like pineapple and mango. These flavors can add a refreshing and vibrant quality to the wine.
- Floral notes: On the other hand, white wines with floral aromas can offer delicate and fragrant characteristics. These may include scents of jasmine, honeysuckle, or orange blossom, providing a more aromatic and elegant experience.
Sweetness vs. Dryness
- Fruit-driven wines often tend to be sweeter, while floral wines are typically drier. Sweetness can enhance the perception of fruit flavors, while dryness can accentuate the floral notes and provide a crisper and refreshing taste.
Understanding the distinction between fruit and floral notes in white wine can help wine enthusiasts appreciate the diversity and complexity of different white wine varieties. Exploring these flavor profiles can lead to a more enjoyable and immersive wine-tasting experience, whether you prefer a fruity or floral white wine.
Aging Potential
What factors impact the aging potential of red and white wines? The aging potential of wines refers to the amount of time they can be stored and matured before they start to deteriorate in quality. Several factors contribute to this potential, including the grape variety, winemaking techniques, and the presence of tannins and acidity. Red wines generally have a higher aging potential than white wines due to their higher tannin and acidity levels.
However, certain white wines like Chardonnay and Riesling can also age well. It is important to note that proper storage conditions, such as temperature and humidity, play a crucial role in maintaining the aging potential of wines. Additionally, serving temperature recommendations should be followed to appreciate the complexities of aged wines fully.
| Factors | Red Wines | White Wines |
|---|---|---|
| Grape Variety | Cabernet Sauvignon, Nebbiolo | Chardonnay, Riesling |
| Tannins | Higher levels | Lower levels |
| Acidity | Higher levels | Lower levels |
| Aging Potential | Generally higher | Variable |
Table: Factors impacting the aging potential of red and white wines.
Serving Temperature Recommendations
To fully appreciate the flavors and nuances of red and white wines, serving them at the appropriate temperature is important. Proper serving temperature can enhance the taste and aroma of the wine, allowing you to experience it at its best. Here is a serving temperature guide to help you enjoy your wines to the fullest:
Chilling Techniques for White Wines:
- Refrigerate white wines at around 45-50°F (7-10°C) to preserve their refreshing acidity and fruity flavors.
- If the wine is too warm, you can quickly chill it by placing the bottle in an ice bucket filled with ice and cold water for about 20 minutes.
Warming Techniques for Red Wines:
- Serve red wines at a slightly cooler than room temperature, around 60-65°F (15-18°C), to bring out their rich flavors and soften the tannins.
- If the wine is too cool, you can warm it up by holding the glass in your hands or decanting it into a decanter and allowing it to sit for a few minutes.
Food Pairing Suggestions
When considering food pairing suggestions for red and white wines, it is important to consider the flavors and characteristics of both types of wine. Red wines are typically bolder and more full-bodied, with flavors like blackberries, cherries, and spice. These wines pair well with richer and heartier dishes, such as grilled meats, stews, and aged cheeses. Some popular red wine regions include Bordeaux in France, Tuscany in Italy, and Napa Valley in California.

On the other hand, white wines are often lighter and more refreshing, with flavors like citrus, apple, and tropical fruits. They pair well with lighter dishes such as seafood, salads, and soft cheeses. Popular white wine regions include Burgundy in France, Marlborough in New Zealand, and Mosel in Germany.
When it comes to wine and cheese pairings, red wines generally pair well with aged and hard cheeses, while white wines complement softer and creamier cheeses. Some classic combinations include pairing a bold red wine with a sharp cheddar or a crisp white wine with a creamy brie.
Health Benefits
Red and white wines offer distinct health benefits that can contribute to overall well-being. Here are some of the health benefits associated with each:
Red Wine
- Rich in antioxidants: Red wine contains resveratrol, a powerful antioxidant that has been linked to various health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer.
- Promotes heart health: Moderate consumption of red wine has been associated with a lower risk of heart disease due to its ability to increase HDL cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol) and improve overall cardiovascular health.
White Wine
- Supports healthy skin: White wine contains antioxidants that can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals, resulting in a more youthful appearance.
- Boosts immune system: The antioxidants present in white wine can help strengthen the immune system, making the body more resilient against infections and diseases.
Both red and white wines have an aging potential, allowing them to develop complex flavors and aromas over time. Remember, moderation is key when it comes to enjoying these health benefits.
Popular Red and White Wine Examples
Various popular examples exist for red and white wines, showcasing the diverse range of flavors and characteristics within each category. Some well-known examples of red wine include Cabernet Sauvignon, Pinot Noir, and Merlot. Cabernet Sauvignon is known for its full-bodied flavor and deep red color, while Pinot Noir is lighter and more delicate. Merlot falls somewhere in between, offering a smooth and velvety texture.
Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, and Riesling are among the favorites for white wine. Chardonnay is often described as rich and buttery, while Sauvignon Blanc is crisp and refreshing. Riesling, on the other hand, is known for its sweet and aromatic profile. These examples highlight the color variations and grape varieties that contribute to the distinct characteristics of red and white wines.
Red and White Wine: Savor the Symphony of Flavors
As we uncork the essence of this delightful journey through the vineyards of knowledge, we must pause to savor the rich bouquet of insights we’ve gathered about red and white wine. From the deep, ruby hues of reds, brimming with tannic tales and bold flavors, to the golden whispers of whites, echoing with crisp acidity and delicate floral notes, we’ve explored the diverse spectrum that these wines paint across our palates and hearts.
Red wines, with their robust character, not only bring warmth to our tables but also carry the legacy of the grapes and the land, encapsulating the mystery of their dark-skinned varieties. They remind us of cozy evenings, filled with hearty meals and rich conversations. Meanwhile, white wines, with their lighter, more refreshing nature, evoke images of sunny afternoons and delicate appetizers, their pale colors mirroring the lightness of a joyful day.
As aficionados or casual sippers, our appreciation for these wines transcends mere taste. It delves into the heart of tradition, culture, and the artistry of winemaking. Understanding their unique attributes – from grape varieties to fermentation processes, from flavor profiles to health benefits – not only enhances our drinking experience but also connects us to a history as old as time.
In every bottle of red or white wine lies a story waiting to be told, a flavor waiting to be discovered, and a moment waiting to be cherished. Whether you’re a seasoned connoisseur or a curious newcomer, the world of red and white wine invites you to embark on an endless journey of discovery and delight.
So, raise your glass to the timeless dance of red and white wines, the symphony of flavors they bring, and the joy they add to our lives. And remember, whether you prefer the boldness of red or the crispness of white, each sip is a celebration of the vine’s bountiful gift.
Cheers to the vibrant red and white wine world – may your exploration be as enriching as the drink itself! 🍷🍇
Frequently Asked Questions About Red and White Wine
Can Red Wine Be Made From White Grapes and Vice Versa?
Red wine production typically involves fermenting red grape varieties with their skins, which gives the wine its characteristic color and tannins. Conversely, white wine is made by fermenting the juice of white grapes without their skins.
What Is the Difference in Alcohol Content Between Red and White Wine?
When comparing the alcohol content between red and white wine, it is important to note that red wines generally have a higher alcohol content than white wines. This difference is influenced by various factors, including the grape variety, fermentation process, and aging techniques employed by winemakers. Additionally, while red wines tend to have bolder flavors with notes of dark fruits and spices, white wines typically exhibit lighter and crisper flavors, often with hints of citrus and floral characteristics. Both types of wine offer unique tasting experiences, catering to different preferences and occasions.
Are There Any Health Benefits Specific to Red or White Wine?
Red and white wine have distinct health benefits. Red wine contains antioxidants like resveratrol, which has been linked to heart health. White wine contains compounds like flavonoids, which may promote lung health. Both wines, when consumed in moderation, can contribute to overall well-being.
Can Red Wine Be Served Chilled Like White Wine?
Red wine can indeed be served chilled, contrary to popular belief. While it is typically enjoyed at room temperature, certain lighter red wines, such as Beaujolais or Pinot Noir, can be enhanced by serving them slightly chilled.
Are There Any Specific Food Pairing Suggestions for Sweet White Wines?
When it comes to sweet white wines, there are several food pairing suggestions that can enhance the overall dining experience. From fruity Rieslings to luscious Sauternes, these wines are best enjoyed with desserts and dishes that complement their sweetness.
Pouring Precision, Savoring Excellence—Encyclopedia Wines. For more fascinating insights into the world of wines, visit encyclopediawines.com.







